Atmospheric Circulation—The Coriolis Effect
Air circulates in the atmosphere forming six different cells, three in each hemisphere. These cells are- the Hadley cell, Ferrel cell, and Polar cell. GEOGRAPHY HOST: Hadley cell, Ferrel cell, Polar cell | Atmospheric circulation
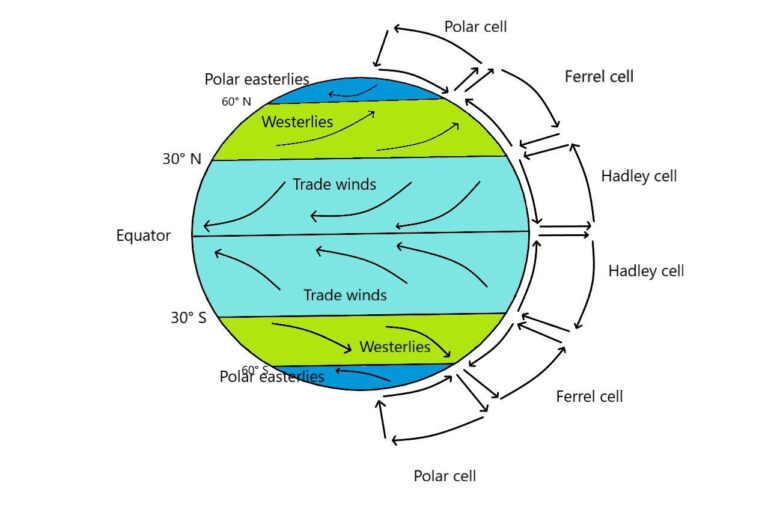
GEOGRAPHY HOST: Hadley cell, Ferrel cell, Polar cell | Atmospheric circulation
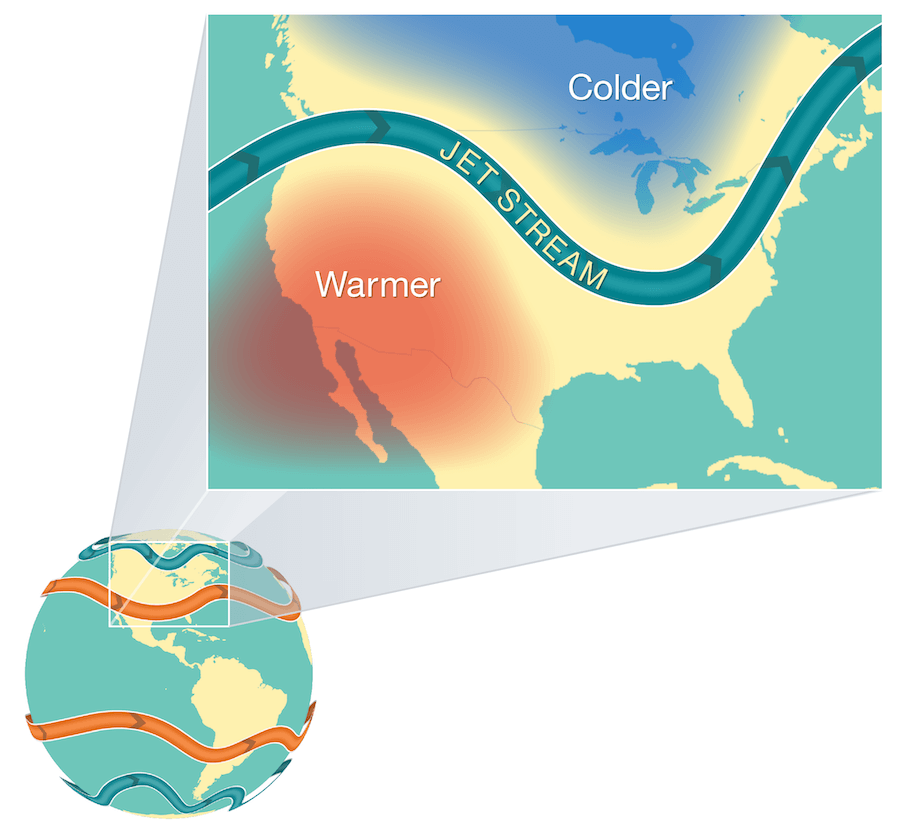
The Jet Streams
The Sun doesn’t heat the whole Earth evenly. That’s why areas near the equator are hot and areas near the poles are cold.
So when Earth’s warmer air masses meet cooler air masses, the warmer air rises up higher in the atmosphere while cooler air sinks down to replace the warm air. This movement creates an air current, or wind. A jet stream is a type of air current that forms high in the atmosphere.
On average, jet streams move at about 110 miles per hour. But dramatic temperature differences between the warm and cool air masses can cause jet streams to move at much higher speeds — 250 miles per hour or faster. Speeds this high usually happen in polar jet streams in the wintertime. NOAA: What Is the Jet Stream?
Global winds drag on the water’s surface, causing it to move and build up in the direction that the wind is blowing. And just as the Coriolis effect deflects winds to the right in the Northern Hemisphere and to the left in the Southern Hemisphere, it also results in the deflection of major surface ocean currents to the right in the Northern Hemisphere (in a clockwise spiral) and to the left in the Southern Hemisphere (in a counter-clockwise spiral). These major spirals of ocean-circling currents are called “gyres” and occur north and south of the equator. They do not occur at the equator, where the Coriolis effect is not present (Ross, 1995). NOAA: Boundary Currents

The warm air of the Gulf Stream supports a subtropical environment for the Isles of Scilly in the Southwest of Great Britain. Learn about the Canary Island date palms on the Isle of Tresco from The International Palm Society.

In contrast, over to the west of the Scilly Islands at the same latitude, polar bears flourish in New Foundland.
The World News: Polar bear breaks into Newfoundland home in terrifying attack
A marauding polar bear that terrorized the tiny community of Goose Cove, Newfoundland, went too far when he broke into the home of the Reardon family.
The 300-pound bear had been traveling from house to house, breaking doors and windows in repeated attempts to get inside. The bear raided a farm, killing a sheep, a lamb and two ducks without bothering to stop and eat the animals.
But on Thursday morning, the polar bear invaded the home of Louis Reardon, 55, in this northern Newfoundland fishing town — and that morning was its last.
The Big Takeaway
The Earth is often compared to a majestic blue marble, especially by those privileged few who have gazed upon it from orbit. This is due to the prevalence of water on the planet’s surface. While water itself is not blue, water gives off blue light upon reflection…In simplest terms, water makes up about 71% of the Earth’s surface, while the other 29% consists of continents and islands…To break the numbers down, 96.5% of all the Earth’s water is contained within the oceans as salt water, while the remaining 3.5% is freshwater lakes and frozen water locked up in glaciers and the polar ice caps. Of that fresh water, almost all of it takes the form of ice: 69% of it, to be exact. Phys.org: What percent of Earth is water?
Greenhouse Gasses
What are greenhouse gases? Greenhouse gases are gases in Earth’s atmosphere that trap heat. They let sunlight pass through the atmosphere, but they prevent the heat that the sunlight brings from leaving the atmosphere. The main greenhouse gases are:
- Water vapor
- Carbon dioxide
- Methane
- Ozone
- Nitrous oxide
- Chlorofluorocarbons
NASA: Meet the Greenhouse Gases!
Climate alarmists develop many pie charts depicting CO2 as the principal greenhouse gas. Comparing the Earth’s atmosphere to a greenhouse’s indoor controlled and confined ‘climate’ is unfortunate and disingenuous. As an aside, greenhouse growers employ CO2 generators to elevate the daytime CO2 concentration to as much as 1,000 ppm.
Atmospheric water, H2O, as vapor and clouds, is by far the most important source of greenhouse warming of the Earth’s surface. Atmospheric CO2 also contributes to greenhouse warming but much less than H2O. More CO2 will cause some additional warming, both directly and with amplification (or possibly attenuation) by feedbacks, which are still very poorly understood. In addition to modest warming from more CO2, the earth’s temperature is affected by many other factors. Among these are solar activity, the distribution of atmospheric water vapor and clouds, atmospheric and ocean circulation patterns, volcanic activity, slow changes in the earth’s orbital parameters. Whether more CO2 will be good or bad for life on earth does not depend on the mere existence of greenhouse warming and related effects from more CO2, like changes in the pH of the oceans, and benefits to plant growth. The issue is the magnitudes of the effects. As detailed [here: A Primer on Carbon Dioxide and Climate], we are persuaded that the net effects of increasing CO2 will be very good for the world, and especially for its human population. Source: CO2 Coalition, June 28, 2022

As you’ve learned, the earth’s peak emission occurs at infrared wavelengths (from Wien’s Law), so what happens to that radiation after it’s emitted upward from the surface? Some is absorbed by air molecules, in particular, so-called “greenhouse gases,” such as water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide. Of the greenhouse gases, water vapor is the most abundant in the atmosphere, followed by carbon dioxide (although recall that in the overall scheme of the atmosphere, these are trace gases). It turns out that some of the wavelengths that carbon dioxide and water vapor absorb readily (particularly those around 15 microns and a little larger) coincide with the wavelengths of earth’s peak emission. Source: Penn State University, Department of Meteorology and Atmospheric Science: The “Greenhouse Effect,” and Global Warming
Want to know more about the cause of the frigid polar vortex that chilled North Texas down to 0°F during the “big chill” of Februrary 2021? Are you perhaps just a little curious about the El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) and what changes the temperature of equitorial water temperature of the Pacific Ocean? If yes, read: Climate emergency? The true peril is information deficit disorder.
Knowledge is power. Ignorance is a choice.
John White
Rockwall, Texas


